We’re a reader-funded news organisation, with more than 1.5 million supporters in 180 countries. With this vital support, our reporting remains fiercely independent, and is never manipulated by commercial or political ties. And it’s free, for everyone. But if you can support us, we need you. Give just once from $1, or better yet, power us every month with a little more. Thank you.
Deep in the Mojave desert, about halfway between Los Angeles and Phoenix, a sparkling blue sea shimmers on the horizon. Visible from the I-10 highway, amid the parched plains and sun-baked mountains, it is an improbable sight: a deep blue slick stretching for miles across the Chuckwalla Valley, forming an endless glistening mirror.
But something’s not quite right. Closer up, the water’s edge appears blocky and pixelated, with the look of a low-res computer rendering, while its surface is sculpted in orderly geometric ridges, like frozen waves.
“We had a guy pull in the other day towing a big boat,” says Don Sneddon, a local resident. “He asked us how to get to the launch ramp to the lake. I don’t think he realised he was looking at a lake of solar panels.”
Over the last few years, this swathe of desert has been steadily carpeted with one of the world’s largest concentrations of solar power plants, forming a sprawling photovoltaic sea. On the ground, the scale is almost incomprehensible. The Riverside East Solar Energy Zone – the ground zero of California’s solar energy boom – stretches for 150,000 acres, making it 10 times the size of Manhattan.
It is a crucial component of the United States’ green energy revolution. Solar makes up about 3% of the US electricity supply, but the Biden administration hopes it will reach 45% by 2050, primarily by building more huge plants like this across the country’s flat, empty plains.
But there’s one thing that the federal Bureau of Land Management (BLM) – the agency tasked with facilitating these projects on public land – doesn’t seem to have fully taken into account: the desert isn’t quite as empty as it thought. It might look like a barren wilderness, but this stretch of the Mojave is a rich and fragile habitat for endangered species and home to thousand-year-old carbon-capturing woodlands, ancient Indigenous cultural sites – and hundreds of people’s homes.
Residents have watched ruefully for years as solar plants crept over the horizon, bringing noise and pollution that’s eroding a way of life in their desert refuge.
“We feel like we’ve been sacrificed,” says Mark Carrington, who, like Sneddon, lives in the Lake Tamarisk resort, a community for over-55s near Desert Center, which is increasingly surrounded by solar farms. “We’re a senior community, and half of us now have breathing difficulties because of all the dust churned up by the construction. I moved here for the clean air, but some days I have to go outside wearing goggles. What was an oasis has become a little island in a dead solar sea.”
Concerns have intensified following the recent news of a project, called Easley, that would see the panels come just 200 metres from their backyards. Residents claim that excessive water use by solar plants has contributed to the drying up of two local wells, while their property values have been hit hard, with several now struggling to sell their homes.

“It has been psychologically gruelling,” says Teresa Pierce, who moved here six years ago. “From the constant pounding of the metal posts to the endless dust storms. I now have allergies that I’d never had before – my arms burn all day long and my nose is always running. I feel like a prisoner in my own home.”
Elizabeth Knowles, director of community engagement for Intersect Power, the company behind the Easley project, said it knew of residents’ concerns and was exploring how to move the project further from the community. “Since being made aware of their concerns, we have been in regular contact with residents to listen to their concerns and incorporate their feedback into our planning efforts.”
‘90% of the story is underground’
The mostly flat expanse south-east of Joshua Tree national park was originally identified as a prime site for industrial-scale solar power under the Obama administration, which fast-tracked the first project, Desert Sunlight, in 2011. It was the largest solar plant in the world at the time of completion, in 2015, covering an area of almost 4,000 acres, and it opened the floodgates for more. Since then, 15 projects have been completed or are under construction, with momentous mythological names like Athos and Oberon. Ultimately, if built to full capacity, this shimmering patchwork quilt could generate 24 gigawatts, enough energy to power 7m homes.
But as the pace of construction has ramped up, so have voices questioning the cumulative impact of these projects on the desert’s populations – both human and non-human.
Kevin Emmerich worked for the National Park Service for over 20 years before setting up Basin & Range Watch in 2008, a non-profit that campaigns to conserve desert life. He says solar plants create myriad environmental problems, including habitat destruction and “lethal death traps” for birds, which dive at the panels, mistaking them for water.
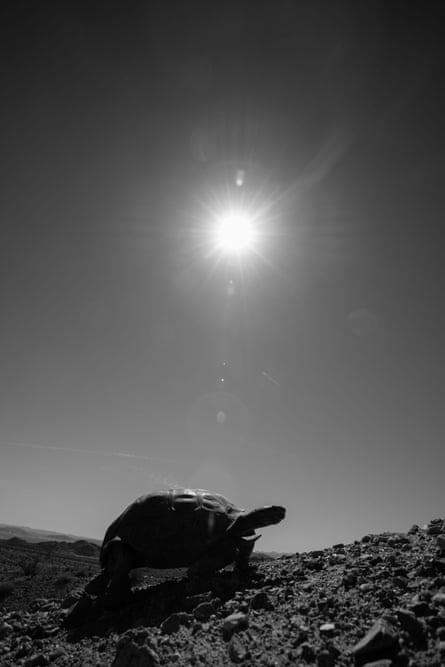
He says one project bulldozed 600 acres of designated critical habitat for the endangered desert tortoise, while populations of Mojave fringe-toed lizards and bighorn sheep have also been afflicted. “We’re trying to solve one environmental problem by creating so many others.”

“The plan talks about the importance of making sure there’s enough room between the solar projects to preserve wildlife routes,” says Chris Clarke of the National Parks Conservation Association. “But the individual assessments for each project do not take into account the cumulative impact. The solar plants are blocking endangered species’ natural transport corridors across the desert.”
Much of the critical habitat in question is dry wash woodland, made up of “microphyll” shrubs and trees like palo verde, ironwood, catclaw and honey mesquite, which grow in a network of green veins across the desert. But, compared with old-growth forests of giant redwoods, or expanses of venerable Joshua trees, the significance of these small desert shrubs can be hard for the untrained eye to appreciate.
“When people look across the desert, they just see scrubby little plants that look dead half the time,” says Robin Kobaly, a botanist who worked at the BLM for over 20 years as a wildlife biologist before founding the Summertree Institute, an environmental education non-profit. “But they are missing 90% of the story – which is underground.”
Her book, The Desert Underground, features illustrated cross-sections that reveal the hidden universe of roots extended up to 150ft below the surface, supported by branching networks of fungal mycelium. “This is how we need to look at the desert,” she says, turning a diagram from her book upside-down. “It’s an underground forest – just as majestic and important as a giant redwood forest, but we can’t see it.”
The reason this root network is so valuable, she argues, because it operates as an enormous “carbon sink” where plants breathe in carbon dioxide at the surface and out underground, forming layers of sedimentary rock known as caliche. “If left undisturbed, the carbon can remain stored for thousands of years,’” she says.
Desert plants are some of the oldest carbon-capturers around: Mojave yuccas can be up to 2,500 years old, while the humble creosote bush can live for over 10,000 years. These plants also sequester carbon in the form of glomalin, a protein secreted around the fungal threads connected to the plants’ roots, thought to store a third of the world’s soil carbon. “By digging these plants up,” says Kobaly, “we are removing the most efficient carbon sequestration units on the planet – and releasing millennia of stored carbon back into the atmosphere. Meanwhile, the solar panels we are replacing them with have a lifespan of around 25 years.”

“The history of the world is told by these sites,” he says, “by geoglyphs, petroglyphs, and pictographs. Yet the government has chosen to ignore and push aside the creation story in the name of progress.”
Residents feel trapped and choked by dust, while experts warn environmental damage is ‘solving one problem by creating others’
Deep in the Mojave desert, about halfway between Los Angeles and Phoenix, a sparkling blue sea shimmers on the horizon. Visible from the I-10 highway, amid the parched plains and sun-baked mountains, it is an improbable sight: a deep blue slick stretching for miles across the Chuckwalla Valley, forming an endless glistening mirror.
But something’s not quite right. Closer up, the water’s edge appears blocky and pixelated, with the look of a low-res computer rendering, while its surface is sculpted in orderly geometric ridges, like frozen waves.
“We had a guy pull in the other day towing a big boat,” says Don Sneddon, a local resident. “He asked us how to get to the launch ramp to the lake. I don’t think he realised he was looking at a lake of solar panels.”

Over the last few years, this swathe of desert has been steadily carpeted with one of the world’s largest concentrations of solar power plants, forming a sprawling photovoltaic sea. On the ground, the scale is almost incomprehensible. The Riverside East Solar Energy Zone – the ground zero of California’s solar energy boom – stretches for 150,000 acres, making it 10 times the size of Manhattan.
It is a crucial component of the United States’ green energy revolution. Solar makes up about 3% of the US electricity supply, but the Biden administration hopes it will reach 45% by 2050, primarily by building more huge plants like this across the country’s flat, empty plains.
But there’s one thing that the federal Bureau of Land Management (BLM) – the agency tasked with facilitating these projects on public land – doesn’t seem to have fully taken into account: the desert isn’t quite as empty as it thought. It might look like a barren wilderness, but this stretch of the Mojave is a rich and fragile habitat for endangered species and home to thousand-year-old carbon-capturing woodlands, ancient Indigenous cultural sites – and hundreds of people’s homes.
Residents have watched ruefully for years as solar plants crept over the horizon, bringing noise and pollution that’s eroding a way of life in their desert refuge.
“We feel like we’ve been sacrificed,” says Mark Carrington, who, like Sneddon, lives in the Lake Tamarisk resort, a community for over-55s near Desert Center, which is increasingly surrounded by solar farms. “We’re a senior community, and half of us now have breathing difficulties because of all the dust churned up by the construction. I moved here for the clean air, but some days I have to go outside wearing goggles. What was an oasis has become a little island in a dead solar sea.”
Concerns have intensified following the recent news of a project, called Easley, that would see the panels come just 200 metres from their backyards. Residents claim that excessive water use by solar plants has contributed to the drying up of two local wells, while their property values have been hit hard, with several now struggling to sell their homes.

“It has been psychologically gruelling,” says Teresa Pierce, who moved here six years ago. “From the constant pounding of the metal posts to the endless dust storms. I now have allergies that I’d never had before – my arms burn all day long and my nose is always running. I feel like a prisoner in my own home.”
Elizabeth Knowles, director of community engagement for Intersect Power, the company behind the Easley project, said it knew of residents’ concerns and was exploring how to move the project further from the community. “Since being made aware of their concerns, we have been in regular contact with residents to listen to their concerns and incorporate their feedback into our planning efforts.”
‘90% of the story is underground’
The mostly flat expanse south-east of Joshua Tree national park was originally identified as a prime site for industrial-scale solar power under the Obama administration, which fast-tracked the first project, Desert Sunlight, in 2011. It was the largest solar plant in the world at the time of completion, in 2015, covering an area of almost 4,000 acres, and it opened the floodgates for more. Since then, 15 projects have been completed or are under construction, with momentous mythological names like Athos and Oberon. Ultimately, if built to full capacity, this shimmering patchwork quilt could generate 24 gigawatts, enough energy to power 7m homes.
But as the pace of construction has ramped up, so have voices questioning the cumulative impact of these projects on the desert’s populations – both human and non-human.
Kevin Emmerich worked for the National Park Service for over 20 years before setting up Basin & Range Watch in 2008, a non-profit that campaigns to conserve desert life. He says solar plants create myriad environmental problems, including habitat destruction and “lethal death traps” for birds, which dive at the panels, mistaking them for water.
He says one project bulldozed 600 acres of designated critical habitat for the endangered desert tortoise, while populations of Mojave fringe-toed lizards and bighorn sheep have also been afflicted. “We’re trying to solve one environmental problem by creating so many others.”


Such adverse impacts are supposed to be prevented by the desert renewable energy conservation plan (DRECP), which was approved in 2016 after years of consultation and covers almost 11m acres of California. But Emmerich and others think the process is flawed, allowing streamlined environmental reviews and continual amendments that they say trample conservationists’ concerns.
“The plan talks about the importance of making sure there’s enough room between the solar projects to preserve wildlife routes,” says Chris Clarke of the National Parks Conservation Association. “But the individual assessments for each project do not take into account the cumulative impact. The solar plants are blocking endangered species’ natural transport corridors across the desert.”

Much of the critical habitat in question is dry wash woodland, made up of “microphyll” shrubs and trees like palo verde, ironwood, catclaw and honey mesquite, which grow in a network of green veins across the desert. But, compared with old-growth forests of giant redwoods, or expanses of venerable Joshua trees, the significance of these small desert shrubs can be hard for the untrained eye to appreciate.
“When people look across the desert, they just see scrubby little plants that look dead half the time,” says Robin Kobaly, a botanist who worked at the BLM for over 20 years as a wildlife biologist before founding the Summertree Institute, an environmental education non-profit. “But they are missing 90% of the story – which is underground.”
Her book, The Desert Underground, features illustrated cross-sections that reveal the hidden universe of roots extended up to 150ft below the surface, supported by branching networks of fungal mycelium. “This is how we need to look at the desert,” she says, turning a diagram from her book upside-down. “It’s an underground forest – just as majestic and important as a giant redwood forest, but we can’t see it.”
The reason this root network is so valuable, she argues, because it operates as an enormous “carbon sink” where plants breathe in carbon dioxide at the surface and out underground, forming layers of sedimentary rock known as caliche. “If left undisturbed, the carbon can remain stored for thousands of years,’” she says.
Desert plants are some of the oldest carbon-capturers around: Mojave yuccas can be up to 2,500 years old, while the humble creosote bush can live for over 10,000 years. These plants also sequester carbon in the form of glomalin, a protein secreted around the fungal threads connected to the plants’ roots, thought to store a third of the world’s soil carbon. “By digging these plants up,” says Kobaly, “we are removing the most efficient carbon sequestration units on the planet – and releasing millennia of stored carbon back into the atmosphere. Meanwhile, the solar panels we are replacing them with have a lifespan of around 25 years.”

For Alfredo Acosta Figueroa, the unstoppable march of desert solar represents an existential threat of a different kind. As a descendant of the Chemehuevi and Yaqui nations, he has watched as what he says are numerous sacred Indigenous sites have been bulldozed.
“The history of the world is told by these sites,” he says, “by geoglyphs, petroglyphs, and pictographs. Yet the government has chosen to ignore and push aside the creation story in the name of progress.”
His organisation, La Cuna de Aztlan, acts as custodian of over 300 such sites in the Lower Colorado River Basin, many of which, he says, have already been damaged beyond repair. He claims that a 200ft-long geoglyph of Kokopelli, a flute-playing god, was destroyed by a new road to one of the solar plants, while an image of Cicimitl, an Aztec spirit said to guide souls to the afterlife, is also threatened. “The solar projects cannot destroy just one sacred site without destroying the sacredness of the entire area,” he adds. “They are all connected.”

He cites a 2010 report by the California Energy Commission, which includes testimony from the heritage experts Dr Elizabeth Bagwell and Beverly E Bastian stating that “more than 800 sites within the I-10 Corridor and 17,000 sites within the Southern California Desert Region will potentially be destroyed”, and that “mitigation can reduce the impact of the destruction, but not to a less-than-significant level”.
The Bureau of Land Management declined a request for an interview. In an emailed statement, its public affairs officer, Michelle Van Der Linden, did not directly address questions about solar plants’ water use, health issues, or ecological and archeological impacts, but said the agency operated within the applicable laws and acts. “The DRECP effort was a multiple-year collaborative discussion resulting in an agreement reached between the BLM, numerous environmental groups, partners and stakeholders, in regards to the application and decision process related to renewable energy projects. Project issues were and continue to be identified and addressed through the National Environmental Policy Act process, which includes the opportunity for public engagement and input and also addresses many of the cumulative impacts and additional environmental, social and economic concerns mentioned.”
‘So many other places we should put solar’

But a more fundamental question remains: why build in the desert, when thousands of acres of rooftops in urban areas lie empty across California?
“There are so many other places we should be putting solar,” says Clarke, of the National Parks Conservation Association, from homes to warehouses to parking lots and industrial zones. He describes the current model of large-scale, centralised power generation, hundreds of miles from where the power is actually needed, as “a 20th-century business plan for a 21st-century problem”.
“The conversion of intact wildlife habitat should be the absolute last resort, but it’s become our first resort – just because it’s the easy fix.”
Vincent Battaglia, founder of Renova Energy, a rooftop solar company based in Palm Desert, agrees. “We’ve been led to believe that all solar is good solar,” he says. “But it’s not when it molests pristine land, requires hundreds of millions of dollars to transmit to city centres, and loses so much power along the way. It is simply preserving the monopoly of the big energy companies.”
California recently reduced the incentive for homeowners to install rooftop solar panels after it slashed the amount that they can earn from feeding power back into the grid by about 75%. Forecasters suggest that, after doubling in size from 2020 to 2022, the market for residential solar installations is expected to decrease by nearly 40% by 2024 as a result.
Battaglia is optimistic that home energy storage is the answer. “Batteries are the future,” he says. “With solar panels on rooftops and batteries in homes, we’ll finally be able to cut the cord from the big utility companies. Soon, those fields of desert solar farms will be defunct – left as rusting relics of another age.”
Back in Lake Tamarisk, the residents are preparing for the long battle ahead. “They picked on a little town and thought they could wipe us out,” says Sneddon. “But they can’t just mow us over like they did the desert tortoises.
“They thought we were a bunch of uneducated redneck hicks living out here in the desert,” says Pierce. “We’re going to show them they were wrong.”






 Tucker Carlson home studio reportedly dismantled byFox News workers
Tucker Carlson home studio reportedly dismantled byFox News workers