
The United States’ power grid, once a marvel of 20th-century engineering, is now teetering on the edge of collapse. As demand surges from emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, data centers, and electric vehicles, an aging infrastructure struggles to keep up. Recent blackouts, escalating costs, and regulatory bottlenecks are painting a picture of a system pushed to its limits. This article explores the crisis, what investors should watch for moving forward, and the ripple effects on everyday consumers, drawing on expert analysis and recent data.
The Cracks in the Foundation: Why the Grid is Failing
Are you Paying High Taxes in New Jersey, New York, or California?
America’s electrical grid was largely built in the mid-20th century, with much of its transmission and distribution infrastructure now over 50 years old. According to recent reports, the grid faces unprecedented stress from a combination of factors. Electricity demand is skyrocketing: AI data centers alone consumed about 4.4% of U.S. electricity in 2023, a figure projected to triple by 2028. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) forecasts electricity sales to climb from 4,097 billion kWh in 2024 to 4,193 billion kWh in 2025, equivalent to adding the power needs of seven Seattle-sized cities in the next decade.
Extreme weather exacerbates the vulnerabilities. Heatwaves in Texas and storms in California have triggered widespread blackouts, reminiscent of the 2003 Northeast blackout that left 50 million people in the dark. Cybersecurity threats and physical attacks on substations are on the rise, with the Department of Homeland Security emphasizing the grid’s critical status. Supply chain issues further compound the problem: lead times for large power transformers have stretched beyond 30 months by mid-2025, delaying essential upgrades.
Regulatory hurdles add to the chaos. Transmission projects face five-to-seven-year delays due to permitting issues, jurisdictional disputes between utilities, states, and federal agencies, and policy gridlock. The CIRCUIT Act, introduced in February 2025 to boost domestic transformer production, remains stalled in Congress. Deloitte estimates that the U.S. power sector will require $1.4 trillion in new capital investments between 2025 and 2030 just to maintain reliability.
Investment Opportunities: Where to Look as the Crisis Unfolds
For investors, this gridlock isn’t just a headache—it’s a goldmine of opportunities. The push for modernization and reliability will favor certain sectors over others. Here’s what to watch:
Behind-the-Meter Solutions and Companies
As the centralized grid falters, decentralized “behind-the-meter” technologies—such as battery storage, microgrids, and rooftop solar—are gaining traction. These solutions allow businesses and households to generate and store power independently, reducing reliance on the main grid. Companies like Fluence Energy, Stem Inc., and Tesla Energy are poised for growth, with demand surging for their storage systems to handle peak loads from data centers and EVs. The Department of Energy (DOE) is allocating $32 million in 2025 for smart EV charging and distributed energy integration, signaling federal support. Investors should eye firms innovating in energy management software and modular storage, as these could see explosive adoption in high-demand regions like Northern Virginia, which handles 70% of global internet traffic.
Natural Gas and Oil Companies
Reliability is king in a strained grid, and fossil fuels still provide the backbone. With coal plants retiring (e.g., Utah’s 1,800 MW Intermountain Power Project), natural gas and oil are stepping in as “bridge” fuels. The DOE has delayed retirements of coal and gas plants to avert shortages. Natural gas firms benefit from their flexibility and lower emissions profile compared to coal, while oil companies could see upticks in backup generation demand. Look for integrated energy giants with strong midstream assets, as they can capitalize on rising wholesale prices in deregulated markets like Texas and Arizona, where cooling demands are surging.
Grid UtilitiesTraditional utilities are investing heavily to shore up the system. The DOE aims to boost long-distance transmission capacity by 16% by 2030 through 7,500 miles of new lines. Companies like NextEra Energy, Dominion Energy, and Avangrid are leading the charge—Avangrid, for instance, plans $20 billion in investments across 23 states through 2030. These regulated utilities offer stable dividends and exposure to rate hikes as costs pass through to consumers. Independent power producers like NRG Energy are also attractive, profiting from elevated wholesale electricity prices amid supply constraints. In summary, a diversified approach makes sense: behind-the-meter for growth potential, natural gas/oil for reliability plays, and utilities for steady returns. However, risks like regulatory changes and supply chain disruptions loom large—focus on companies with strong balance sheets and innovation pipelines.
How Consumers Will Feel the Pinch
The grid’s woes will hit consumers hardest through higher bills and unreliable service. As utilities pass on upgrade costs, residential electricity prices are climbing nationwide—up about 6.5% from May 2024 to May 2025. Blackouts could become more frequent, disrupting daily life, work, and safety, especially in vulnerable areas prone to weather extremes. The impact varies by state, with some already facing exorbitant rates due to reliance on imported fuels, geography, or high demand. Below is a table of the top 10 most expensive states for residential electricity, based on EIA data for June 2025 (in cents per kWh). These states, often coastal or isolated, illustrate the uneven burden.
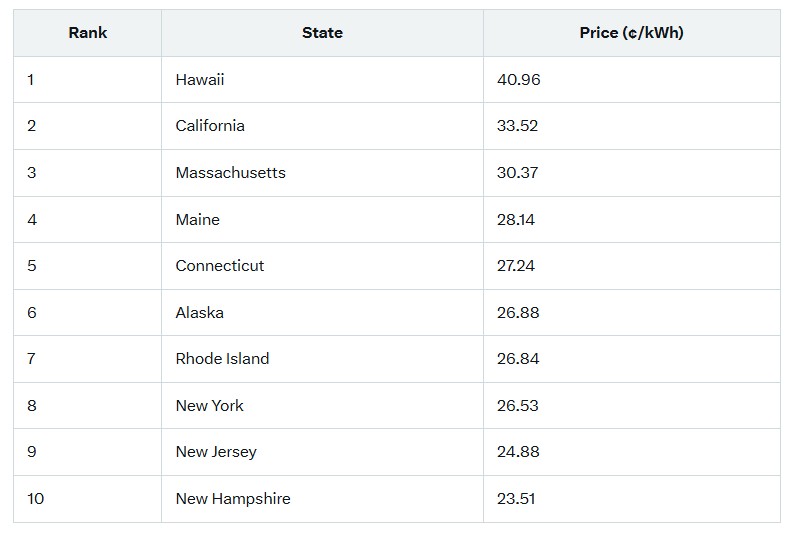
Consumers in these states could see monthly bills exceed $200 for average usage, prompting shifts toward energy efficiency, solar adoption, or even relocation. Nationally, a Microsoft and Google-backed report warns of a shortage of 500,000 electricians in the next decade, further delaying home upgrades and EV installations.
Looking Ahead: A Call for Action
America’s grid crisis demands urgent investment and policy reform to avert catastrophe. While challenges mount, they also herald a transformation toward a smarter, more resilient energy system. Investors who position themselves wisely—balancing innovation with reliability—stand to benefit, but only if policymakers act swiftly. For consumers, the message is clear: prepare for higher costs and potential disruptions by exploring personal energy solutions today.
Avoid Paying Taxes in 2025
Crude Oil, LNG, Jet Fuel price quote
ENB Top News
ENB
Energy Dashboard
ENB Podcast
ENB Substack






