The largest gasoline pipeline in the U.S. is returning to service following a cyberattack that took the fuel artery offline for five days, offering hope that fuel shortages in several states will soon come to an end.
Colonial Pipeline Co., operator of a conduit that handles more fuel than Germany consumes, said it began to resume shipments around 5 p.m. Eastern time Wednesday. In a further effort to provide relief, the Biden administration temporarily waived century-old shipping restrictions to allow one foreign-flagged ocean-going tanker to help relieve the shortages.
U.S. Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm said Tuesday it would take days to fully restore supplies after the pipeline’s restart, while Colonial indicated it will get its physical operations up and running ahead of its business systems. Using foreign-flagged tankers may help in the relief effort, but the sailing time alone for a ship to take fuel from Houston to New York would take six or seven days.
“Resumption of flows is the start, but the race to logistically replenish retail gas stations is the next step,” said Michael Tran, an analyst at RBC Capital Markets. “The restarting of the Colonial pipeline is the beginning of the end of the crisis, not the end.”
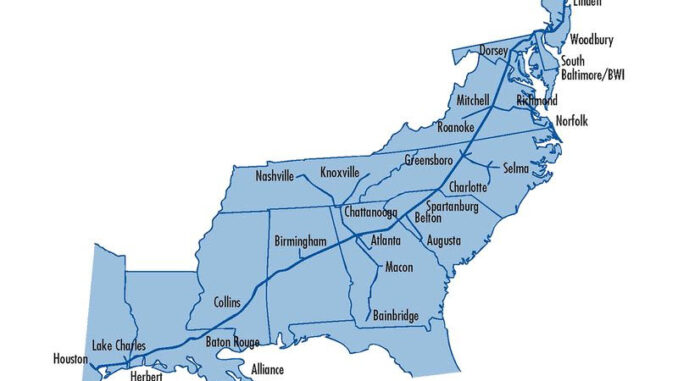
The developments came as gasoline stations were running dry from Florida to Virginia after Colonial was forced to take systems offline on May 7. In parts of the U.S. South, three in every four gas stations had no fuel as of Wednesday, while in Washington, D.C., cars were lining up for blocks as they waited to fill up.
The White House said Colonial’s announcement “means there’s an end in sight for the supply disruptions.” President Joe Biden is also urging Americans “to just purchase what they need, and not hoard fuel, as supply is restored,” Press Secretary Jen Psaki said in a statement Thursday.
Jones Act
The administration temporarily issued a waiver to the 101-year-old Jones Act for one unidentified company. The act stipulates goods transported between U.S. ports be carried on ships built in the U.S. and crewed by American workers.
Widspread waiving of the requirements could allow foreign-flagged tankers to help fill the supply gap left by the interruption to the pipeline. The initial waiver is for one tanker although more are under consideration, a White House official said. Typical cargo deliveries into the U.S. East Coast are about 300,000 barrels.
Earlier this week, the White House announced several other measures to blunt the crisis, including waiving some gasoline requirements and empowering 10 states to allow heavier-than-normal truck loads of fuels.
Despite the improved outlook, the disruption underscores just how vulnerable America’s fuel supply system has become in the wake of increased attacks on energy infrastructure by hackers over the past few years. Colonial is only the latest example of critical infrastructure being targeted by ransomware. Hackers are increasingly attempting to infiltrate essential services such as electric grids and hospitals.
The attack on Colonial also came just as the nation’s energy industry is preparing for summer travel and as fuel demand rebounds from pandemic-related lockdowns. It was reminiscent of a 2018 cyberattack that brought down a third-party communications system used by several natural gas pipelines operators across the U.S.
Colonial normally ships about 2.5 million barrels (105 million gallons) each day, an amount that exceeds the entire oil consumption of Germany. It warned the line may go down again from time to time during the restart process.
Feeling Relief
As the pipeline resumes, the states suffering from the most acute shortages may start to feel relief this weekend.
In North Carolina, some fuel supply should appear right away, said Gary Harris, executive director of the North Carolina Petroleum & Convenience Marketers, a trade association. “People will have to be running trucks a lot to just catch up because so much is out at this time,” he said.
Major branded stations will get fuel first as they are under contract with suppliers, said Harris. Fuel may still be scarce for independent stations that are not under contract.
The ransomware attack that shut down the nation’s biggest fuel pipeline prompted an all-too familiar question in the corridors of power in Washington and boardrooms across the country:
Can anyone stop debilitating hacks?https://t.co/2Wlvit4MRz— Bloomberg Quicktake (@Quicktake) May 12, 2021
In Virginia, consumers should be able to see a difference by Monday, said Michael O’Connor, president of the Virginia Petroleum & Convenience Marketers Association.
This isn’t the first time Colonial has been forced to shut down. In 2016, an explosion kept the system offline for days, raising gasoline prices and forcing the New York Harbor market to become more dependent on imports of fuel from overseas.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation attributed the attack on Colonial to ransomware created by a group called DarkSide. Some evidence emerged linking DarkSide to Russia or elsewhere in Eastern Europe. Biden said Russia has “some responsibility” to address the attack but stopped short of blaming the Kremlin, saying “there’s evidence” the hackers or the software they used are “in Russia.”



